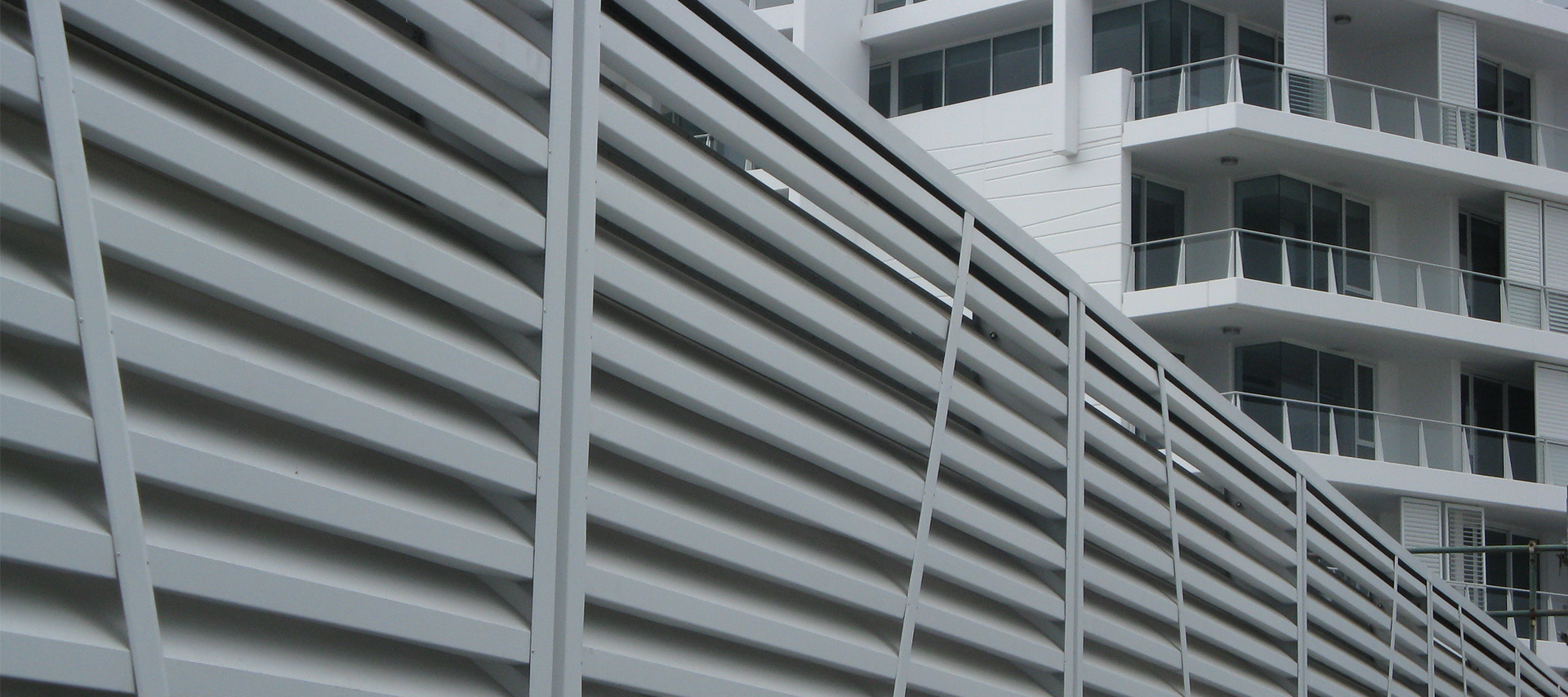
Hush® Acoustic Louvres
Overview
Reduce noise pollution and control noise leakage while taking advantage of natural ventilation capabilities with Hush® High Performance Acoustic Wall Louvres. Our acoustic louvres are engineered and laboratory tested in accordance with AS 1191-2002 to provide advanced noise reduction, while meeting the needs for airflow and providing rain defence.
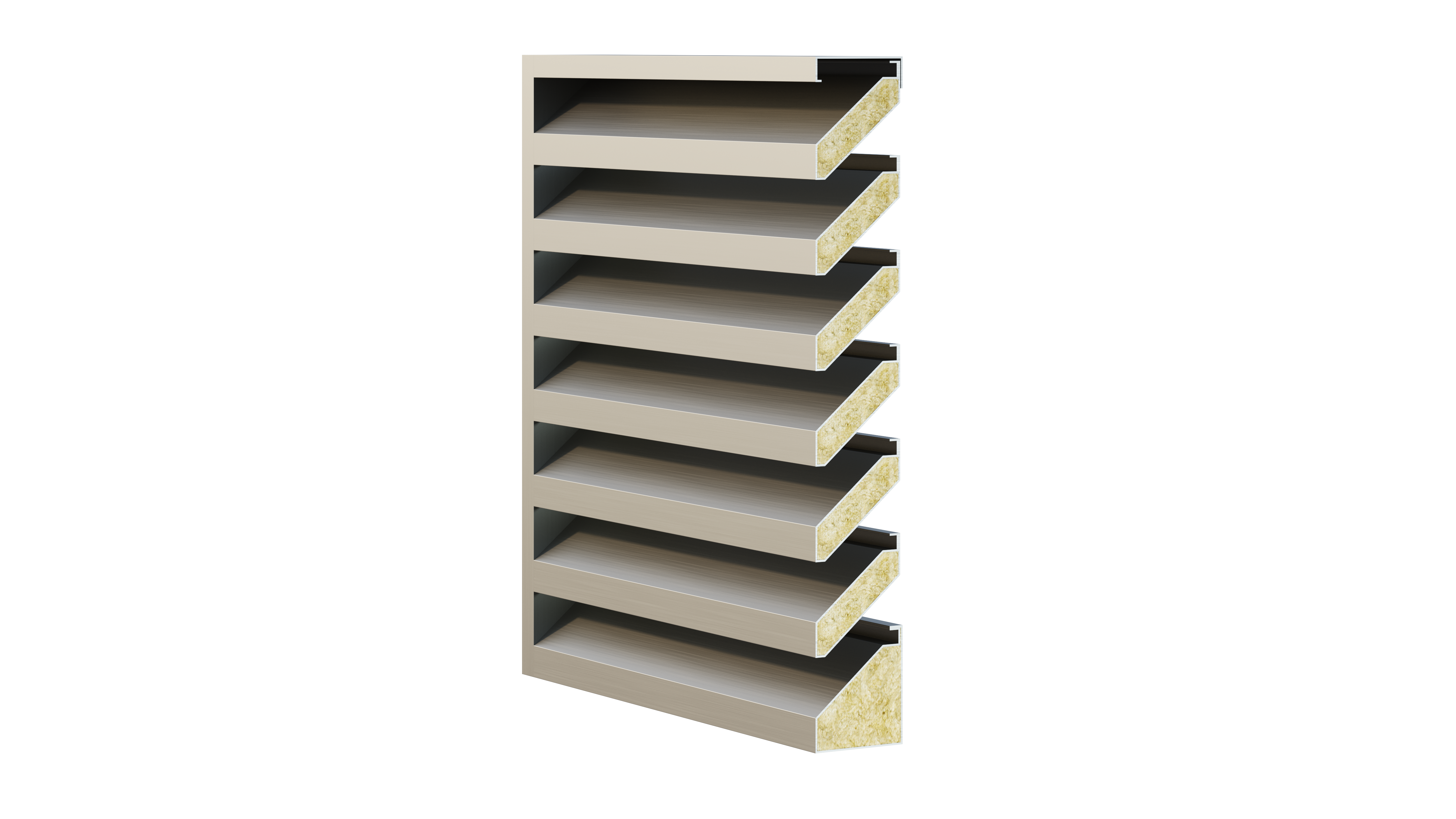
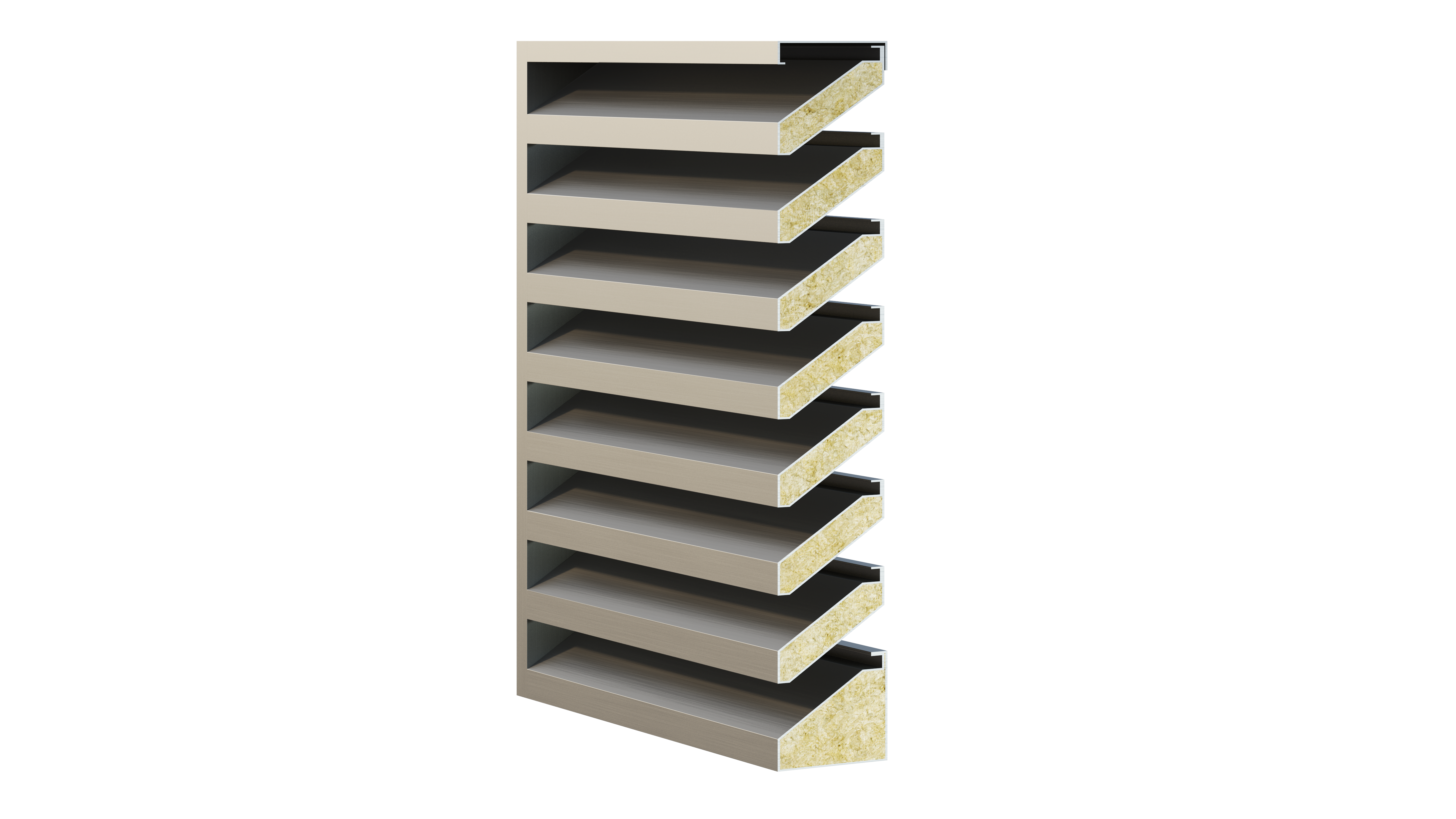
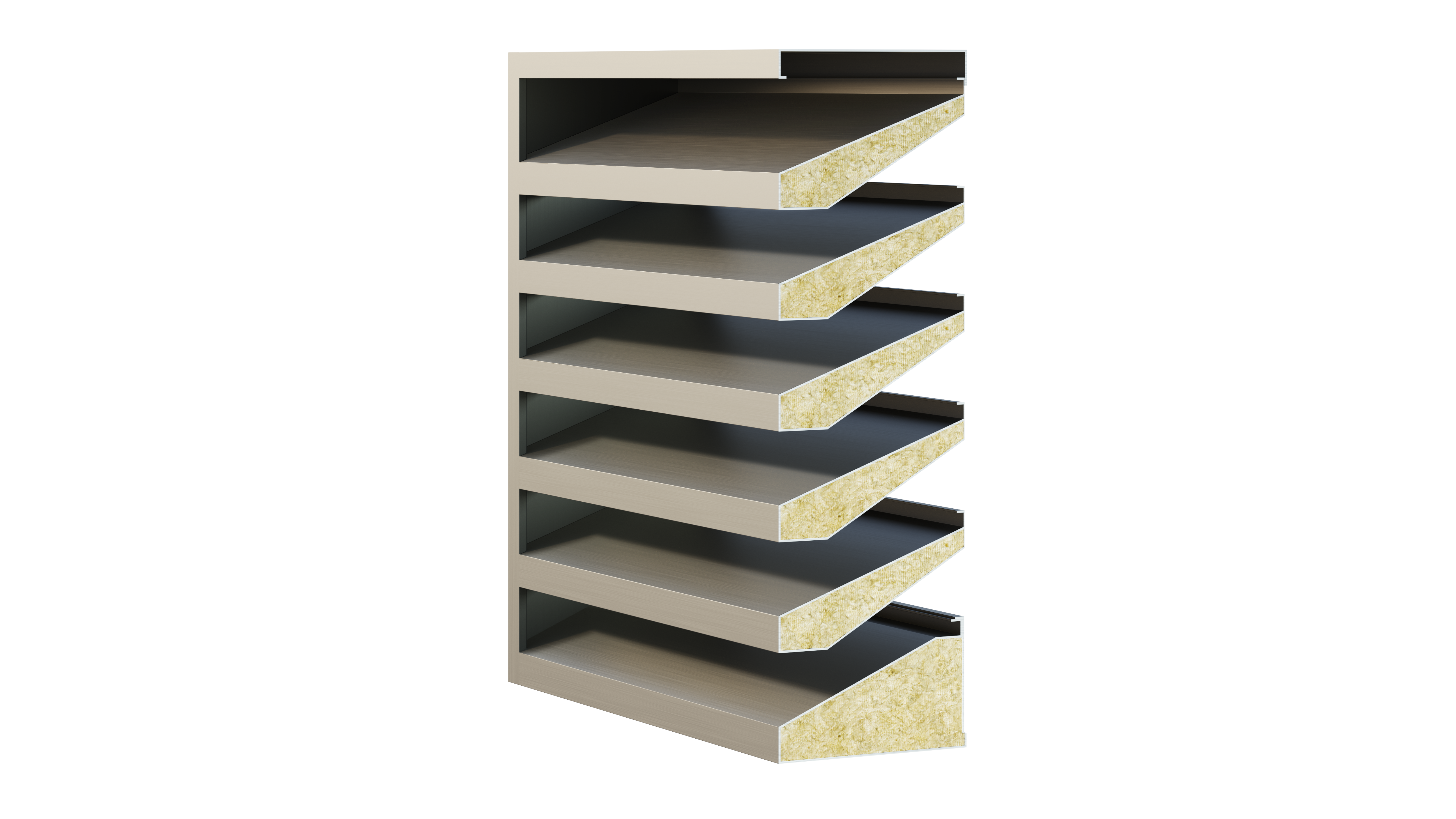
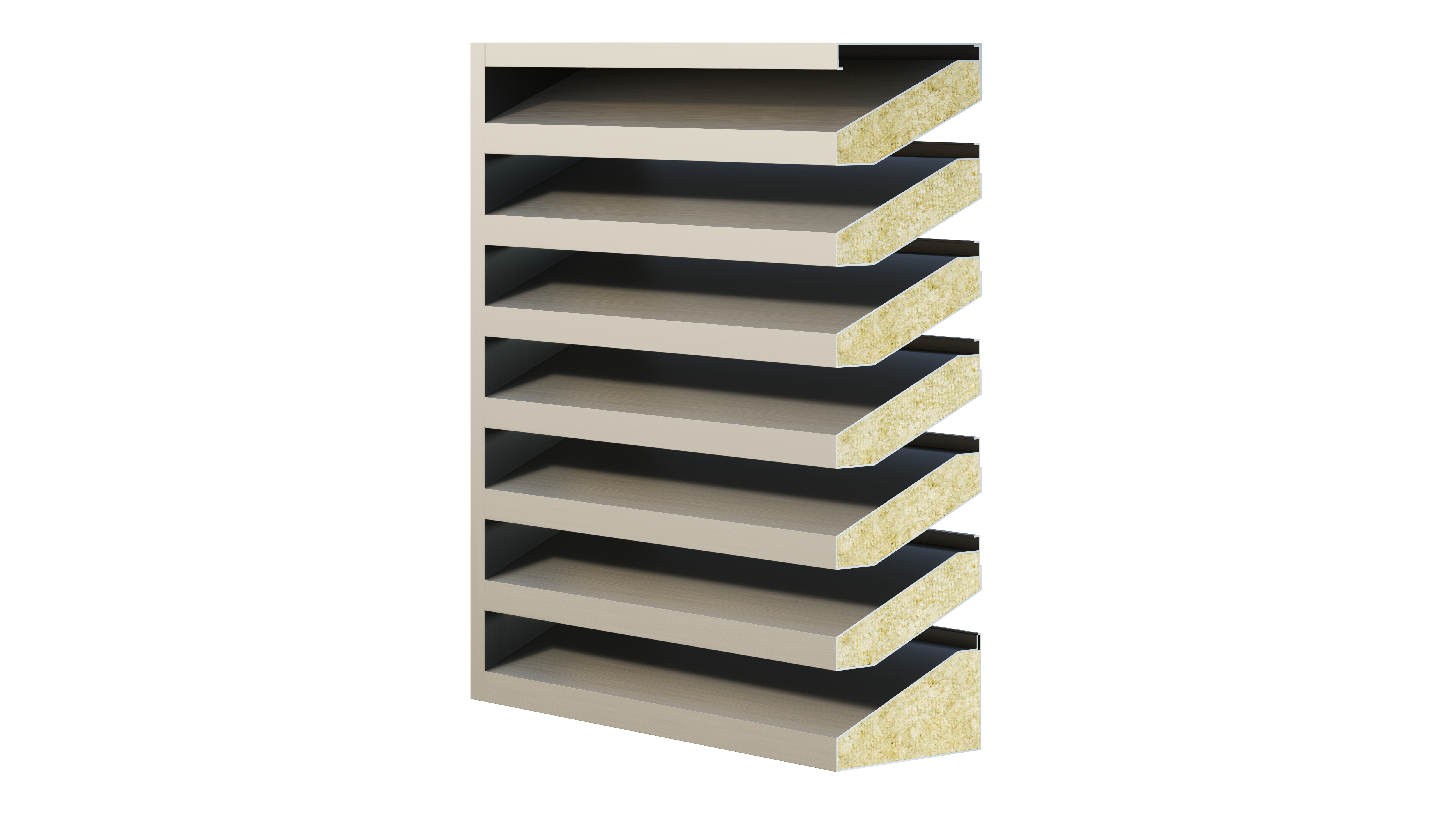
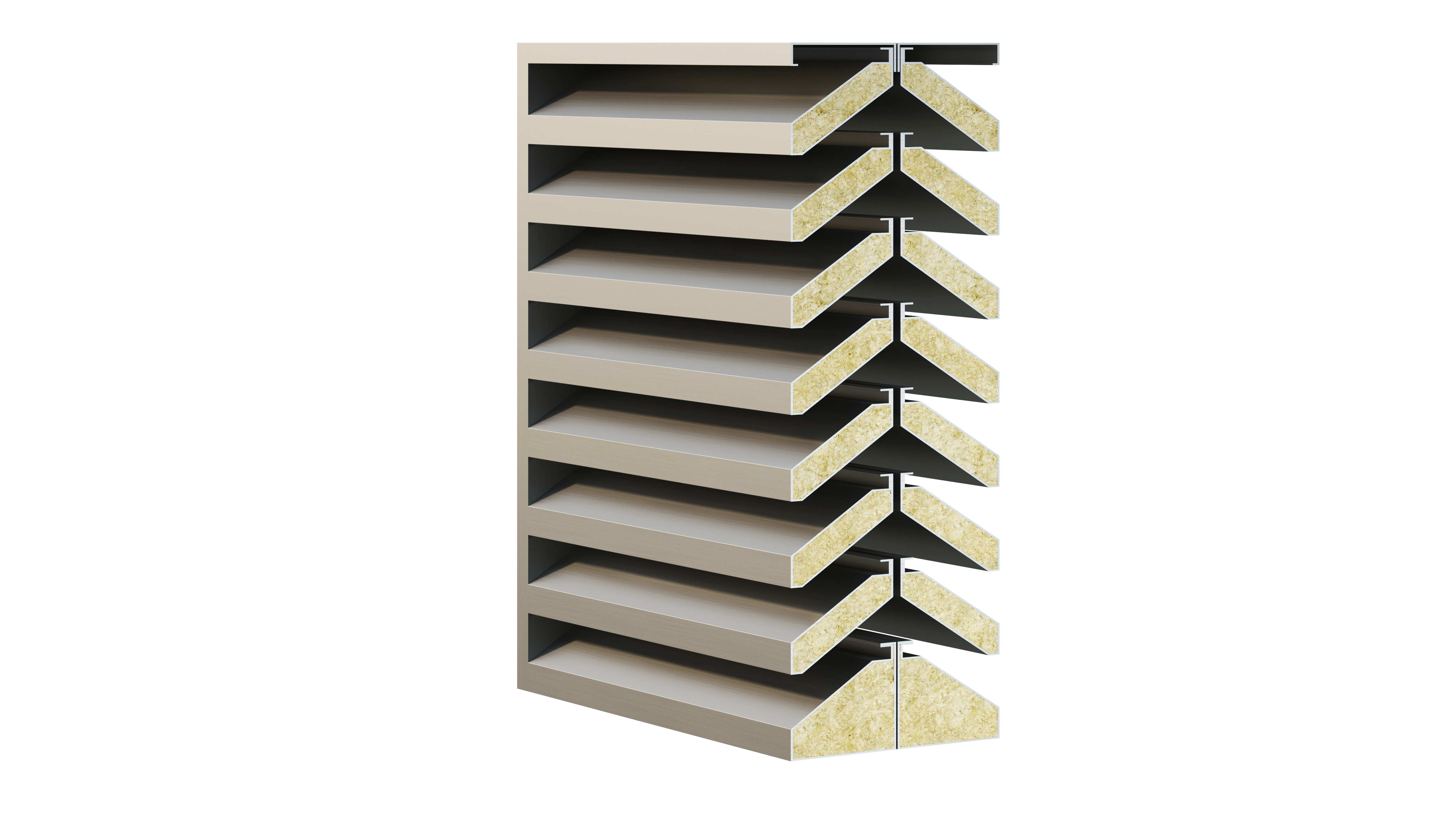
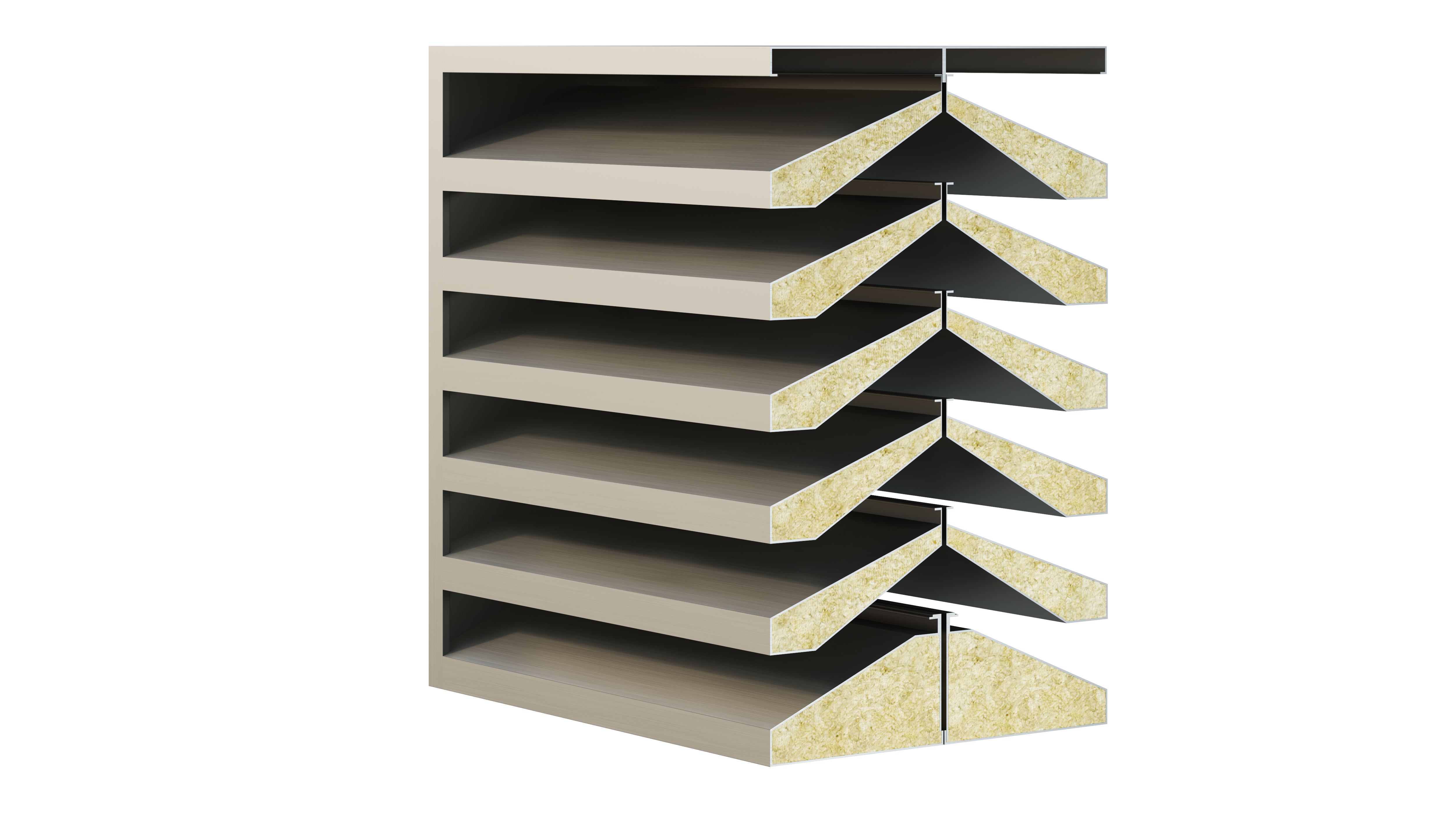

Features
Importance of Acoustic Wall Louvres
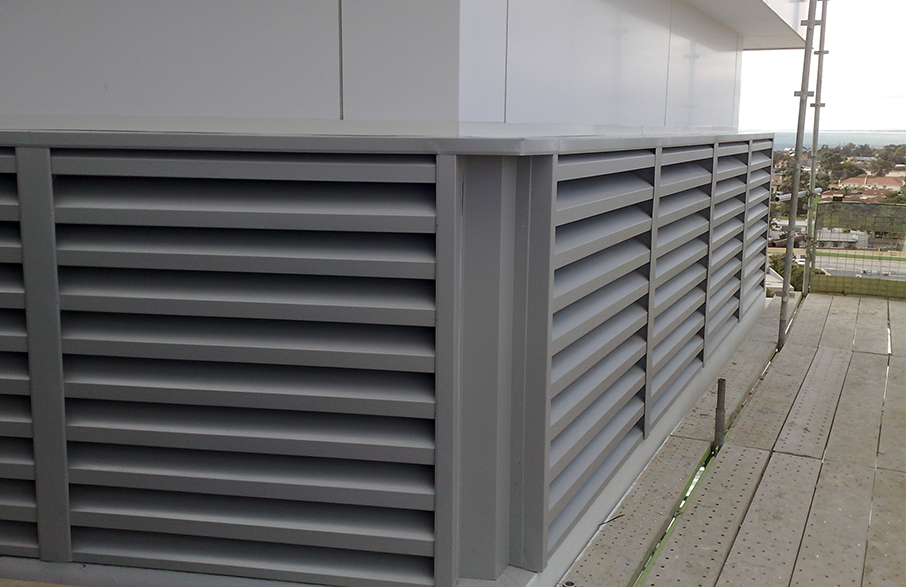

In times of heightened health and safety concerns and requirements, it is important to ensure all noise generating equipping is provided with suitable containment and enclosures to apprehend the sound levels close to the source. Enclosures and containments can lead to stifling the required airflow around the noise generating equipment resulting in low productivity and high maintenance costs. The Hush® acoustic products ensure that the correct airflow is maintained across the equipment and ensuring that the sound levels are acceptable for workplace health.

Acoustic Certification
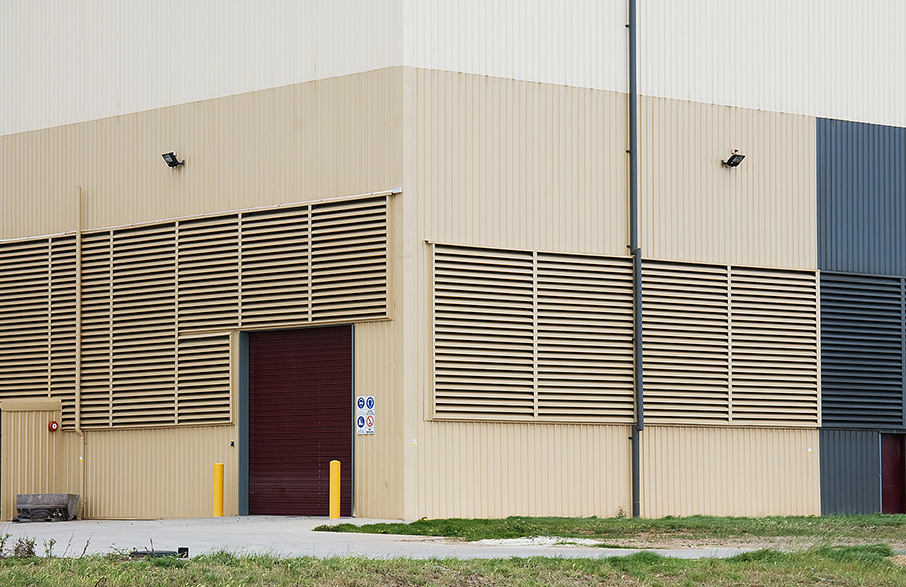

When selecting an acoustic louvre, it is important to ensure the louvre is tested to AS 1191. To achieve this testing a certified laboratory should be used where relevant calibrated instrumentation in accordance with Australian Standards is used. There are many measures which are used such as Rw, Insertion Loss, Noise Reduction, Sound Transmission Loss, and Sound Transmission Constant which may cause confusion to specifiers. There are a range of reasons to use different measures however the Insertion Loss and Noise Reduction measures truly allow a specifier to consider the right product to select over a range of frequencies they may be dealing with on a project. Arcadia have experience and expertise using all measures and are available to assist engineers, HVAC specialists and specifiers with product selection.

Airflow Performance
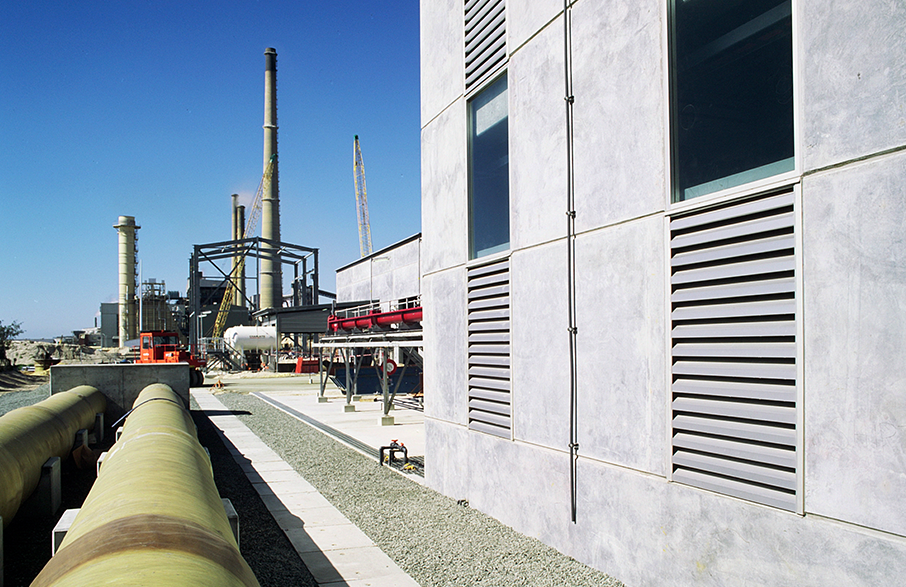

Louvre airflow performance measures the ability of the air to pass through the louvre. Performance is affected by a range of physical elements including the louvre blade configuration, the louvre depth, the quantity of passes (single or double stages), the louvre blade shape and any protrusions that interfere with the free flow of the air. Increased air velocity may cause varying areas of turbulence and flow disturbance which affect the louvre performance. A higher coefficient of discharge results in lower pressure drop over the face velocity meaning more effective air flow performance.

Applications








